Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) software is a digital tool designed to streamline the management of workplace safety, health, and environmental compliance. It replaces outdated manual processes like paper-based forms and spreadsheets with a centralized platform that automates critical tasks. By integrating data, analytics, and real-time monitoring, EHS software helps organizations ensure regulatory compliance, reduce workplace risks, and enhance operational efficiency. This article explores the core functionalities, applications, and considerations for adopting EHS software, drawing from industry insights to provide a clear understanding of its role in modern workplaces.
What EHS Stands For
EHS refers to Environment, Health, and Safety, a multidisciplinary framework focused on protecting employees, workplaces, and the environment. The components are:
- Environment: Encompasses the physical workspace and external surroundings, including air quality, noise levels, and environmental impact.
- Health: Focuses on employee physical and mental well-being, addressing occupational health risks and wellness programs.
- Safety: Involves measures to prevent accidents, injuries, and hazardous incidents through protocols and risk mitigation.
Some organizations extend EHS to include Sustainability (EHSS), incorporating efforts to minimize environmental footprints. Regulatory bodies like OSHA in the United States, the Health and Safety Executive in the UK, and ISO standards (e.g., ISO 14001 and ISO 45001) set guidelines to ensure consistent safety and environmental practices globally.
Core Functions of EHS Software
EHS software consolidates various processes into a unified platform, enabling organizations to manage safety and compliance efficiently. The following sections detail its primary functions, which are central to its value in workplace management.
Incident and Accident Management
EHS software facilitates the reporting and tracking of workplace incidents, such as injuries, near-misses, and accidents. It allows real-time documentation, enabling safety teams to log events as they occur. Automated notifications can alert managers to incidents, ensuring swift follow-up actions. The software also supports corrective action tracking, helping organizations address root causes and prevent recurrence. Centralized data storage ensures that incident records are accessible for analysis and regulatory reporting.
Risk Assessment and Hazard Analysis
Risk assessments are critical for identifying potential workplace hazards. EHS software streamlines this process by providing digital templates for job hazard analyses and risk evaluations. Users can create, assign, and review assessments remotely, with centralized dashboards offering an overview of risk levels across the organization. This functionality helps safety teams prioritize mitigation strategies and maintain a proactive approach to hazard management.
Regulatory Compliance Tracking
Compliance with local and international regulations is a cornerstone of EHS management. EHS software centralizes compliance data, including permits, audits, and policy updates. It enables organizations to schedule inspections, track regulatory deadlines, and generate audit-ready reports. Some platforms integrate with regulatory libraries, providing access to up-to-date standards like OSHA or ISO 45001, ensuring businesses remain compliant and avoid penalties.
Training and Certification Management
Employee training is essential for maintaining safety standards. EHS software tracks training completion, certifications, and compliance requirements. It supports e-learning modules, allowing organizations to deliver tailored safety courses. Features like automated reminders and progress tracking ensure employees stay current with protocols, while some platforms offer just-in-time learning through QR codes for immediate access to safety resources.
Document Management and Control
EHS software provides a cloud-based repository for safety documents, such as safety data sheets (SDS), policies, and incident reports. This centralization eliminates the need for physical filing systems, reducing the risk of lost or outdated records. Authorized users can access documents remotely, ensuring critical information is available when needed, whether on-site or in the field.
Reporting and Analytics
Data-driven decision-making is a key benefit of EHS software. Interactive dashboards visualize safety performance metrics, such as incident rates or compliance status. Analytics tools identify trends, such as recurring hazards in specific areas, enabling proactive interventions. Reports can be shared with stakeholders or regulatory bodies, simplifying communication and ensuring transparency.
Chemical and Hazardous Materials Management
For industries handling hazardous materials, EHS software tracks storage, usage, and disposal. It maintains databases for safety data sheets and supports workflows for managing chemical-related incidents. This functionality ensures compliance with regulations governing hazardous substances and reduces risks associated with improper handling.
Sustainability and Environmental Management
Some EHS platforms include tools for monitoring environmental impact, such as waste emissions or resource usage. These features help organizations align with sustainability goals and comply with environmental regulations like ISO 14001. By tracking metrics like carbon footprints, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship.
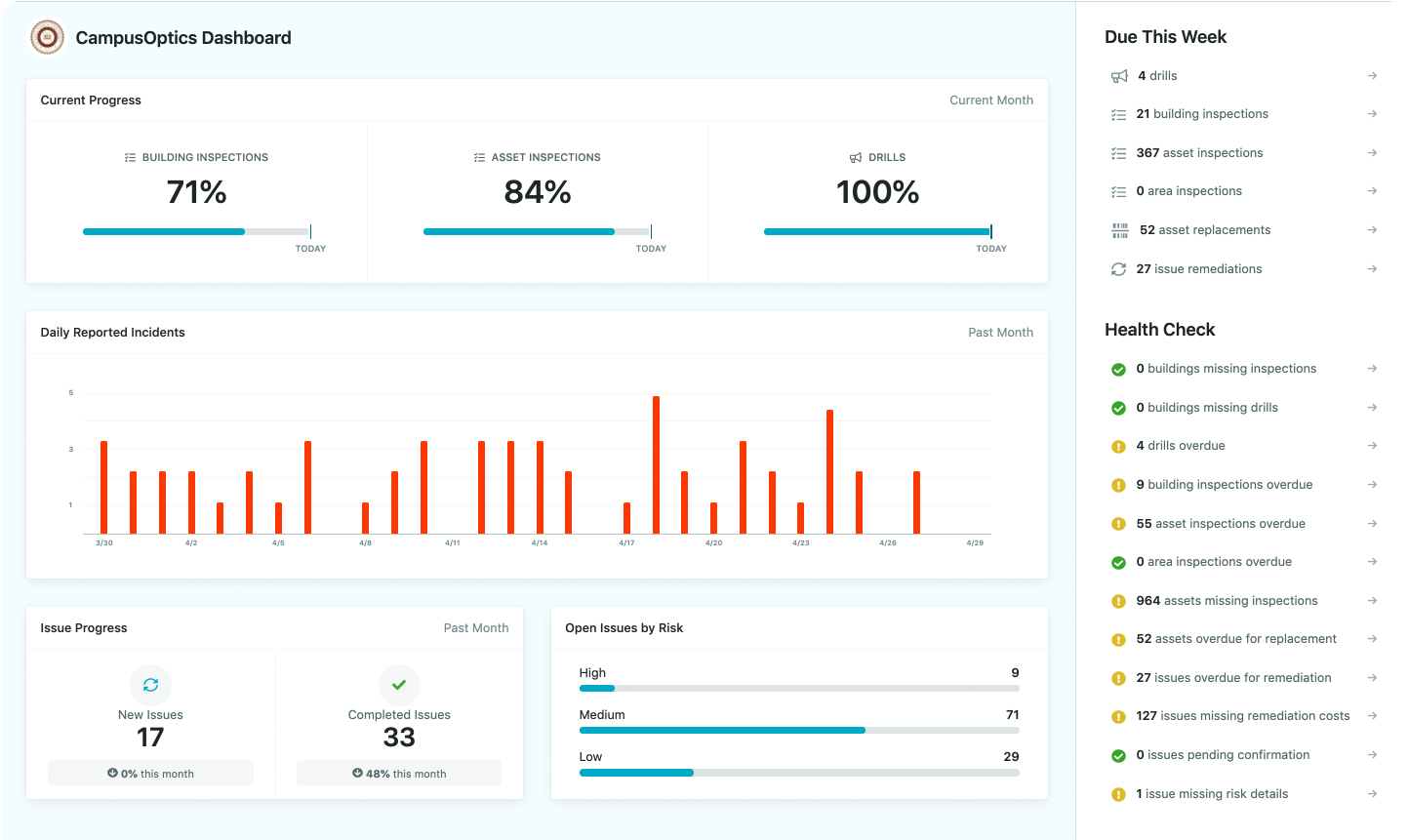
CampusOptics: EHS Software for Higher Education
At CampusOptics, we recognize the unique safety challenges faced by universities, from managing lab chemicals to ensuring campus-wide emergency preparedness. Our EHS software, designed specifically for higher education, centralizes incident reporting, compliance tracking, and risk management into a single platform, fostering collaboration among safety professionals, risk managers, and emergency planners. By integrating these functions, we help institutions reduce risks and build a stronger safety culture, tailored to the dynamic needs of campus environments.
Our platform stands out in the EHS software landscape with its mobile-first approach and data visualization tools. Available on iOS and Android, our app supports on-the-go tasks like scanning barcodes for chemical inventories, capturing photos during inspections, or logging issues via talk-to-text. We also provide real-time mapping of safety assets like AEDs or emergency phones, making critical resources accessible to staff and responders. With quick implementation, configurable permissions, and seamless integration, CampusOptics ensures that EHS processes are practical, scalable, and aligned with the goal of creating safer campuses.
Why Organizations Adopt EHS Software
Organizations across industries adopt EHS software to address the limitations of manual safety management. Traditional methods, such as paper forms or fragmented spreadsheets, are prone to errors, difficult to scale, and time-consuming. EHS software offers a centralized, automated alternative that enhances efficiency and safety. Below are the primary reasons organizations invest in these platforms.
Transition from Manual to Digital Processes
Manual processes, like handwritten incident reports or physical audit files, create inefficiencies and risks of data loss. EHS software digitizes these tasks, enabling real-time data entry and access. Cloud-based platforms allow remote management, which is critical for organizations with multiple locations or field-based staff. Offline capabilities ensure functionality in areas with limited connectivity.
Proactive Risk Management
By providing tools for real-time monitoring and analytics, EHS software shifts organizations from reactive to proactive safety management. For example, identifying patterns in near-miss reports can lead to targeted interventions, reducing the likelihood of serious incidents. This approach minimizes workplace disruptions and enhances employee safety.
Enhanced Compliance and Audit Readiness
Regulatory compliance is a complex challenge, particularly for global organizations. EHS software simplifies compliance by centralizing data and automating reporting. It ensures that audits, permits, and training records are organized and accessible, reducing the risk of non-compliance penalties.
Improved Employee Engagement
EHS software empowers employees to participate in safety processes. Mobile apps simplify incident reporting, requiring only a few taps on a device. Managers can assign tasks and share policy updates, ensuring clarity in responsibilities. This accessibility fosters a culture of safety awareness and accountability.
Key Considerations for Choosing EHS Software
Selecting the right EHS software requires careful evaluation to ensure it aligns with organizational needs. The following factors are critical when making a decision.
Scalability and Customization
As businesses grow, their EHS needs evolve. Scalable software accommodates increasing complexity, such as additional locations or users. Customizable platforms allow organizations to tailor workflows and modules to specific industry requirements or legacy systems.
Interoperability with Existing Systems
Effective EHS software integrates with other operational systems, such as HR platforms or enterprise resource planning tools. Certified APIs enable seamless data exchange, ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure. This interoperability is essential for organizations transitioning from legacy systems.
User Adoption and Training
Successful implementation depends on user acceptance. Software with intuitive interfaces and mobile accessibility encourages adoption. Comprehensive training resources, including e-learning modules and support materials, help employees adapt to the platform. Leadership support is critical to drive adoption across the organization.
Security and Data Protection
Cloud-based EHS software must prioritize data security. Features like encryption and multi-factor authentication protect sensitive information, such as incident reports or compliance data. Robust security measures are particularly important for industries handling hazardous materials or operating in regulated environments.
Vendor Support and Implementation
A reliable vendor provides ongoing support, from implementation to maintenance. Organizations should evaluate vendors based on their track record, customer support quality, and ability to provide tailored solutions. A dedicated implementation team ensures a smooth rollout and maximizes return on investment.
Challenges in Implementing EHS Software
While EHS software offers significant benefits, implementation can present challenges. Transitioning from manual processes requires employee training and change management. Resistance from staff accustomed to legacy systems can hinder adoption. Additionally, integrating new software with existing infrastructure may require technical adjustments. Organizations must secure leadership buy-in to drive cultural change and ensure the platform is fully utilized.
The Role of Leadership in EHS Software Success
Leadership commitment is essential for successful EHS software deployment. Executives must champion the platform, communicating its benefits to employees and aligning it with organizational goals. A dedicated implementation team can facilitate training and address user concerns, ensuring the software becomes a fundamental part of safety management. This top-down approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement and accountability.
Future Trends in EHS Software
The EHS software market is evolving, driven by advancements in technology and industry needs. Integration with Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT and AI, is enhancing real-time monitoring and predictive analytics. Mobile solutions with offline capabilities are becoming standard, supporting field-based operations. Additionally, the focus on sustainability is growing, with platforms incorporating tools to track environmental metrics. These trends indicate a shift toward more integrated, data-driven safety management systems.
Conclusion
EHS software is a transformative tool for managing workplace safety, health, and environmental compliance. By automating processes, providing real-time data, and ensuring regulatory adherence, it enables organizations to create safer, more efficient workplaces. From incident tracking to sustainability management, its features address diverse needs across industries. When selecting EHS software, organizations must consider scalability, interoperability, and user adoption to maximize its impact. With leadership support and a strategic approach to implementation, EHS software can drive lasting improvements in safety and operational performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is EHS software used for?
EHS software manages workplace safety, health, and environmental compliance by automating tasks like incident reporting, risk assessments, and regulatory tracking.
Which industries benefit most from EHS software?
Industries like manufacturing, construction, oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, healthcare, and logistics use EHS software to manage risks and compliance.
How does EHS software improve compliance?
It centralizes compliance data, schedules audits, and generates reports to ensure adherence to regulations like OSHA or ISO standards.
Can small businesses use EHS software?
Yes, EHS software saves time and resources for small businesses, helping them maintain safety and compliance without extensive staff.
What are the key features of EHS software?
Core features include incident management, risk assessments, compliance tracking, training management, document control, and analytics.
How does EHS software support remote work?
Cloud-based platforms and mobile apps enable remote access, offline functionality, and real-time data entry for field-based staff.
What challenges might arise during EHS software implementation?
Challenges include employee resistance, training needs, and integration with existing systems, which require leadership support to overcome.