Chemical inventory management is a structured process for tracking, organizing, and controlling chemicals within facilities such as laboratories, manufacturing plants, and research institutions. It involves maintaining detailed records of chemical quantities, locations, and associated hazards to ensure safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. This article explores the definition, components, benefits, and implementation strategies of chemical inventory management, drawing from established practices in various industries.
Defining Chemical Inventory Management
Chemical inventory management refers to the systematic oversight of chemicals from procurement to disposal. It encompasses the recording of chemical types, quantities, storage conditions, and hazard information in a centralized system. The primary goal is to maintain accurate, up-to-date records to support safe handling, regulatory adherence, and efficient resource use. Unlike manual methods such as spreadsheets, modern systems often leverage specialized software to streamline tracking and reporting processes.
This process is critical in environments where chemicals are used extensively, such as academic laboratories, pharmaceutical companies, and chemical manufacturing facilities. It ensures that personnel have access to necessary materials while minimizing risks associated with improper storage or handling.
Core Components of Chemical Inventory Management
Effective chemical inventory management relies on several key components that work together to maintain control over chemical stocks. These components address tracking, data management, safety, and resource optimization.
Tracking and Monitoring
Tracking involves documenting the movement of chemicals within a facility, from receipt to use or disposal. This includes recording quantities, storage locations, and usage patterns. Advanced systems use barcoding or remote monitoring technologies, such as ultrasonic level sensors, to provide real-time data on inventory levels. These tools help prevent shortages or overstocking by offering accurate insights into stock status.
Data Management
A centralized database is essential for storing comprehensive chemical information. This database typically includes:
- Chemical names and quantities
- Safety Data Sheets (SDS) with hazard details
- Storage locations and conditions
- Expiry dates and CAS numbers
- Usage logs and regulatory classifications
Such systems enable quick access to critical information, supporting decision-making and compliance efforts.
Safety and Compliance
Safety is a cornerstone of chemical inventory management. Systems must ensure that chemicals are stored according to safety standards, such as those set by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) or the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This involves proper labeling, adherence to storage compatibility requirements, and access to hazard information. Compliance with regulations like OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200) is also critical to avoid penalties and ensure workplace safety.
Resource Optimization
By maintaining accurate inventory records, organizations can avoid over-ordering or stockouts. Tracking expiration dates helps reduce waste from spoiled chemicals, while usage data informs procurement decisions. This component enhances operational efficiency by ensuring the right chemicals are available when needed.
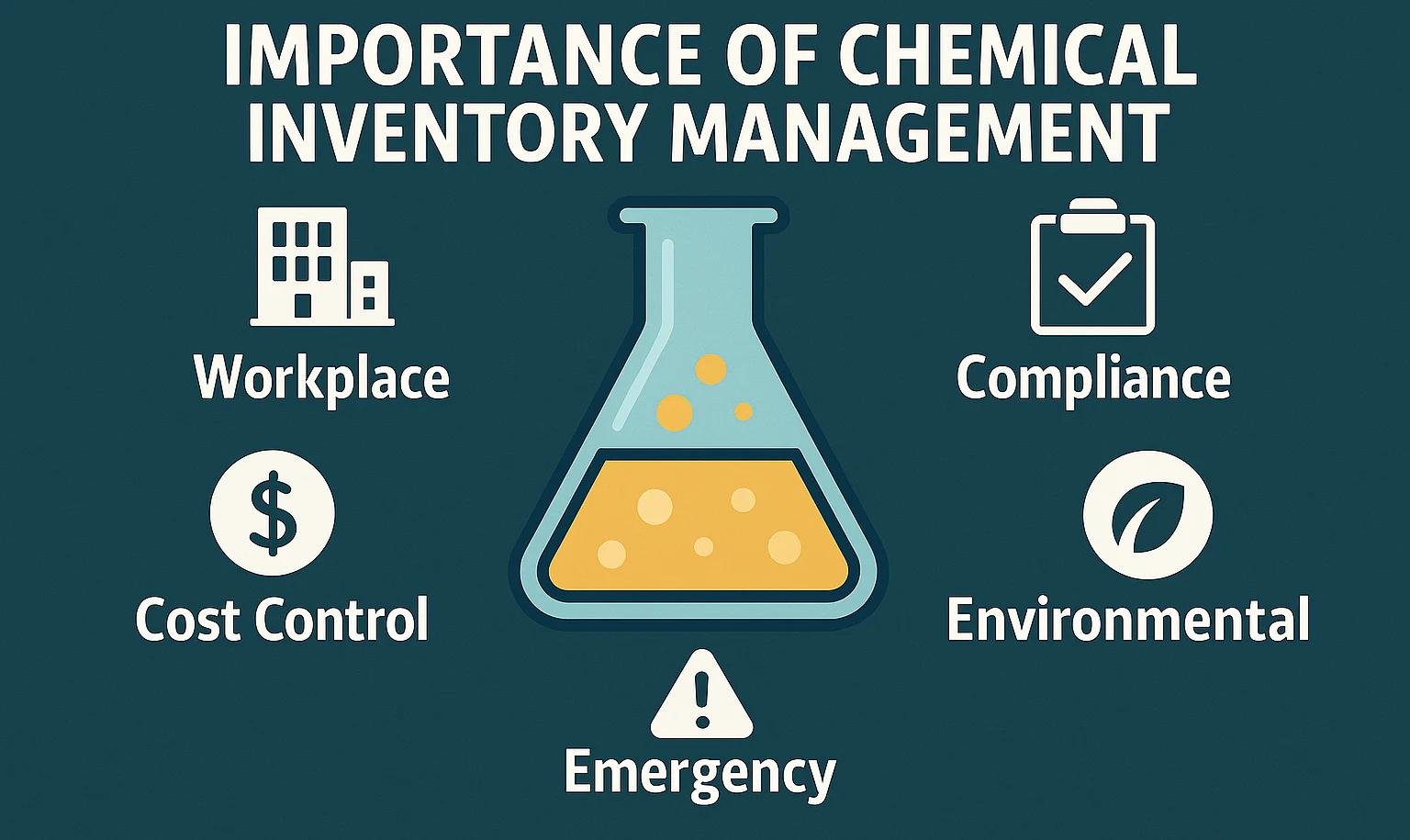
Importance of Chemical Inventory Management
Chemical inventory management is essential for several reasons, each addressing a critical aspect of workplace operations.
Workplace Safety
Improper chemical management can lead to accidents, such as spills, leaks, or exposures, which pose significant risks to personnel. A robust inventory system identifies hazardous materials, ensures proper storage to prevent incompatible chemical reactions, and provides access to safety information like SDS. This reduces the likelihood of workplace incidents and enhances overall safety.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory bodies, including OSHA, EPA, and the Department of Transportation (DOT), impose strict requirements on chemical handling. Organizations must maintain accurate inventory records, proper labeling, and accessible SDS to comply with these standards. Non-compliance can result in fines, legal action, or reputational damage. A well-implemented inventory system streamlines compliance efforts by providing audit-ready documentation.
Cost Control
Maintaining an accurate inventory prevents unnecessary purchases and reduces waste from expired or unused chemicals. By tracking usage patterns, organizations can optimize procurement, leading to cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Environmental Protection
Proper chemical management minimizes the risk of environmental contamination by ensuring safe storage and disposal practices. This supports sustainability goals and reduces the ecological impact of chemical operations.
Emergency Response
In emergencies like fires or spills, rapid access to chemical information is critical. An inventory system provides first responders with details on chemical locations, quantities, and hazards, enabling swift and effective responses.
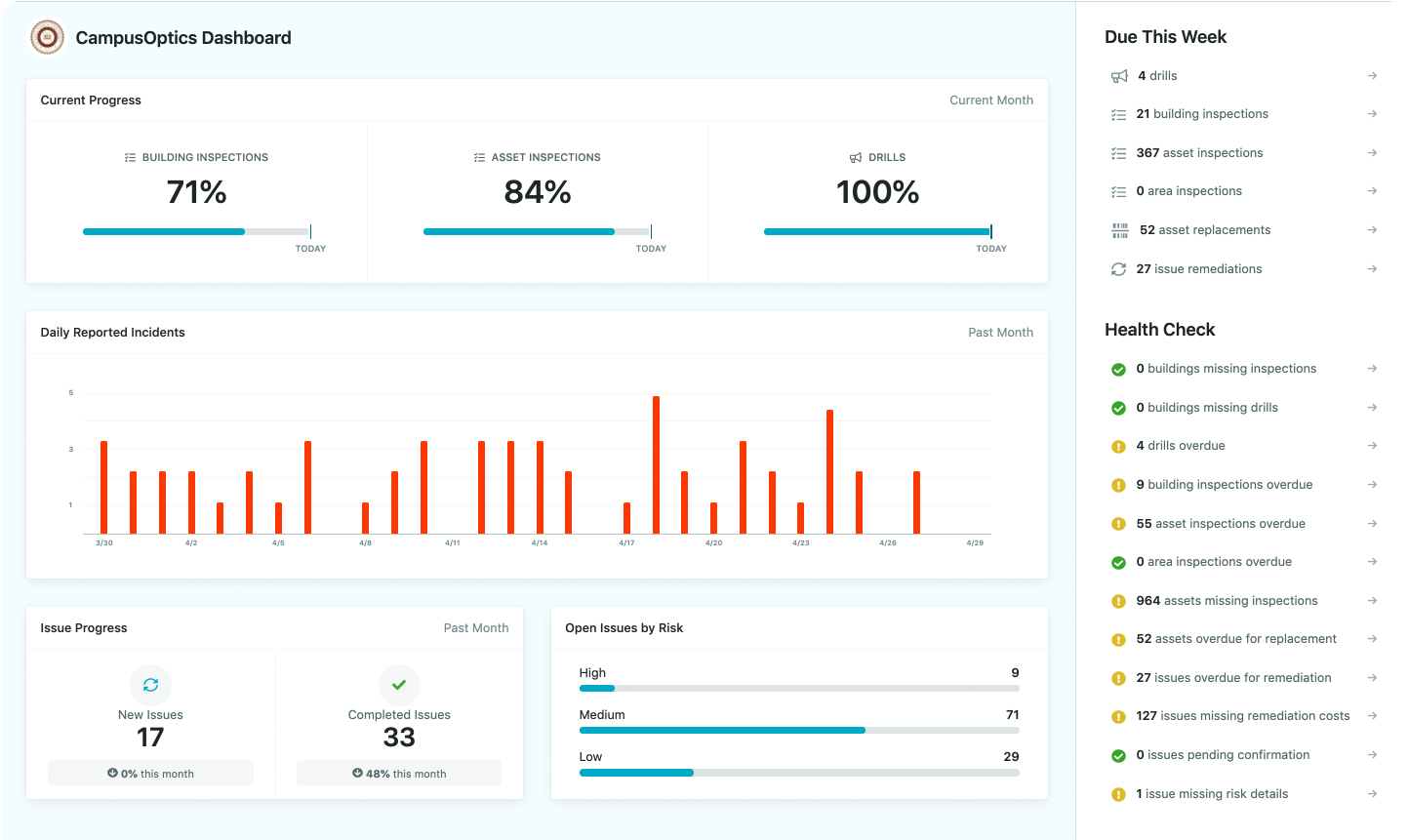
CampusOptics: Tailored EH&S for Higher Education
We designed CampusOptics as a cross-functional EH&S platform specifically for higher education institutions to streamline chemical inventory management and campus-wide safety. Our system integrates chemical tracking with inspections, incident reporting, and safety asset management, helping universities reduce risks and maintain compliance. With our mobile app, available on iOS and Android, we enable staff to scan barcodes on chemical containers, access Safety Data Sheets instantly, and log notes using voice-to-text during inspections, eliminating the need for manual record-keeping.
Our platform also offers data visualization tools, allowing us to map chemical containers, safety assets like AEDs, and emergency phones across campus. We provide turn-key implementation, getting systems operational in weeks, with configurable permissions to ensure the right users access the right data. This approach supports efficient chemical management and enhances safety culture in academic environments.
Benefits of a Chemical Inventory Management System
Implementing a chemical inventory management system offers several advantages that enhance organizational performance.
- Enhanced Safety: Proper storage and handling practices reduce the risk of accidents, such as spills or exposures. Access to hazard information and Safety Data Sheets (SDS) ensures safe chemical use, protecting personnel and facilities from potential harm.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: Automated systems minimize the time spent on manual inventory checks, eliminating repetitive tasks. They prevent redundant purchases and optimize waste disposal, resulting in significant cost savings over time.
- Regulatory Preparedness: Accurate records and comprehensive documentation ensure readiness for audits and inspections. This reduces the risk of non-compliance penalties and simplifies regulatory reporting processes.
- Operational Productivity: Quick access to chemical information allows employees to locate materials efficiently, reducing downtime. This enables staff to focus on core tasks, boosting overall productivity.
- Sustainability: Tracking shelf life and preventing expiration-related disposal minimizes waste. This aligns with sustainability objectives, reducing environmental impact and lowering waste management costs.
Industries Requiring Chemical Inventory Management
Chemical inventory management is critical across various sectors, each with unique needs and regulatory requirements.
Academic Laboratories
Universities and research institutions manage large numbers of chemicals for experiments and studies. Inventory systems help track these materials, ensure compliance with safety standards, and support research accuracy.
Pharmaceutical and Biotech
These sectors require precise inventory control to prevent contamination and meet regulatory requirements. Inventory systems track chemicals used in research, development, and quality assurance processes.
Chemical Manufacturing
Manufacturing facilities rely on inventory systems to manage bulk chemicals, ensuring traceability and reducing waste in production and R&D operations.
Hospitals and Medical Labs
Medical facilities use inventory systems to manage reagents, disinfectants, and hazardous materials, ensuring safe handling and compliance with health regulations.
Food and Beverage Industries
These industries use inventory systems to manage cleaning agents and food-grade chemicals, ensuring compliance with USDA and FDA standards.
Government and Military Facilities
Highly regulated environments require accurate chemical tracking to meet national safety and environmental standards, supporting risk management protocols.
Implementation Strategies
Implementing an effective chemical inventory management system requires careful planning and execution.
Selecting the Right Software
Specialized software, such as ChemSW CISPro Desktop, offers features like barcoding, real-time tracking, and SDS integration. Organizations should choose software that aligns with their specific needs, such as compatibility with existing systems or support for regulatory reporting.
Integrating Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring technologies, such as ultrasonic sensors, provide real-time data on inventory levels. These systems can send automatic alerts when stocks are low, reducing the risk of shortages and minimizing manual checks.
Ensuring Staff Training
Personnel must be trained on system use, safety protocols, and regulatory requirements. This ensures effective adoption and compliance with best practices.
Regular Audits and Updates
Periodic audits of the inventory system ensure data accuracy and compliance. Updating records and reviewing storage conditions help maintain system reliability.
Advanced Features in Modern Systems
Modern chemical inventory management systems leverage cutting-edge technologies to enhance functionality, streamline operations, and improve safety. These advanced features address the evolving needs of organizations handling chemicals, offering tools that go beyond basic tracking to support real-time decision-making, automation, and integration with broader safety protocols. Below, we explore the key advancements that define contemporary systems.
Real-Time Data Access
Cloud-based platforms and mobile applications have transformed how we access chemical inventory data. These tools allow personnel to retrieve up-to-date information on chemical quantities, locations, and safety details from any location, whether in the lab, warehouse, or off-site. By enabling instant access through secure online portals or mobile apps, we can make informed decisions quickly, such as reordering supplies or addressing storage issues. This capability enhances responsiveness, reduces downtime, and supports coordination across departments, ensuring seamless operations in dynamic environments.
Automated Alerts and Notifications
Advanced systems incorporate automated alert mechanisms to proactively manage inventory levels and chemical conditions. We can configure these systems to send notifications for critical events, such as low stock levels, approaching expiration dates, or improper storage conditions. For example, sensors might detect when a chemical container is nearing depletion and trigger an email or app notification to relevant staff. This automation minimizes the risk of operational disruptions and waste, as we can address issues before they escalate, maintaining continuity and compliance.
Contactless Delivery Integration
Integration with hands-free delivery services represents a significant advancement in chemical inventory management. By connecting real-time inventory data to delivery systems, we can automate the scheduling of chemical replenishments based on predefined thresholds. This reduces manual handling of hazardous materials, lowering the risk of exposure or contamination. Additionally, contactless delivery streamlines logistics, as we can coordinate shipments without physical interaction, aligning with safety protocols and improving efficiency in high-volume environments.
Data Visualization and Mapping
Modern systems often include data visualization tools that allow us to map chemical storage locations, safety assets, and potential hazards across a facility. For instance, we can generate visual representations of where chemicals are stored or pinpoint safety equipment like fire extinguishers. These tools support spatial analysis, helping us identify risks, such as incompatible chemical storage, and optimize facility layouts. In academic or large-scale settings, public-facing maps of critical assets can also enhance emergency preparedness, making critical resources easily accessible.
Barcode and QR Code Integration
The use of barcode and QR code scanning has become a standard feature in advanced systems, simplifying inventory tracking. We can use mobile devices to scan codes on chemical containers, instantly retrieving details like quantity, hazard information, or storage requirements. This reduces manual data entry errors and speeds up processes like inventory audits or inspections. By integrating scanning capabilities with mobile apps, we ensure that staff can perform tasks efficiently on the go, maintaining accuracy without being tethered to a desktop system.
Best Practices for Effective Management
To maximize the effectiveness of a chemical inventory system, organizations should adopt the following practices:
- Maintain a centralized database for all chemical information
- Use barcoding or remote monitoring for accurate tracking
- Regularly update SDS and hazard information
- Conduct periodic staff training on system use and safety protocols
- Perform routine audits to ensure data accuracy and compliance
Challenges in Chemical Inventory Management
Implementing and maintaining a chemical inventory management system involves navigating several obstacles that can impact its effectiveness. These challenges, while manageable with proper strategies, require careful consideration to ensure the system delivers its intended benefits. Below, we outline the primary hurdles organizations face and approaches to address them.
Data Accuracy and Consistency
Maintaining accurate and consistent data is a cornerstone of effective chemical inventory management. Errors in data entry, such as incorrect quantities, mislabeled chemicals, or outdated Safety Data Sheets (SDS), can compromise system reliability and lead to safety risks or regulatory non-compliance. These issues often arise from manual input processes or lack of standardized procedures. To mitigate this, we recommend regular audits to verify data accuracy and comprehensive training for staff on proper data entry protocols. Implementing automated tools, such as barcode scanning or remote sensors, can further reduce human error by streamlining data collection.
System Integration with Existing Infrastructure
Integrating a new chemical inventory system with existing organizational infrastructure can be complex, particularly in facilities with legacy software or diverse operational workflows. Compatibility issues may arise when trying to connect inventory systems with procurement, safety, or enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms. This can lead to data silos or inefficiencies if not addressed properly. We advise selecting software solutions designed for interoperability and working with vendors experienced in custom integrations. Conducting thorough compatibility assessments before implementation can help identify potential issues early, ensuring a smoother transition.
Cost of Implementation and Maintenance
The initial investment for a chemical inventory management system, including software acquisition, hardware, and staff training, can be substantial. Ongoing maintenance costs, such as system updates and technical support, may also strain budgets, particularly for smaller organizations. Despite these upfront expenses, the long-term benefits-such as reduced waste, fewer compliance penalties, and improved operational efficiency-often outweigh the costs. To manage this challenge, we suggest conducting a cost-benefit analysis to prioritize features that align with organizational needs and exploring scalable solutions that allow gradual implementation to spread costs over time.
Staff Adoption and Training
Ensuring staff adopt and effectively use a new inventory system can be difficult, especially in environments with high turnover or resistance to change. Without proper training, employees may revert to old habits, such as manual record-keeping, undermining the system’s benefits. We find that comprehensive, ongoing training programs tailored to different user roles-such as lab technicians, safety officers, or procurement staff-can drive adoption. Additionally, involving employees early in the implementation process and demonstrating the system’s practical benefits, like time savings, can foster buy-in and ensure consistent use across the organization.
Conclusion
Chemical inventory management is a critical process for organizations handling chemicals, ensuring safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. By implementing structured systems with robust tracking, data management, and safety protocols, facilities can mitigate risks, reduce costs, and enhance productivity. Advanced technologies, such as real-time monitoring and automated alerts, further streamline operations, while adherence to best practices ensures long-term reliability. As industries continue to prioritize safety and sustainability, effective chemical inventory management remains an essential component of responsible chemical handling.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a chemical inventory management system?
A chemical inventory management system is a software platform designed to track, store, and manage information about chemicals, including quantities, locations, and hazard details.
Why is chemical inventory management important?
It ensures workplace safety, regulatory compliance, cost control, environmental protection, and efficient emergency response by maintaining accurate chemical records.
What industries benefit from chemical inventory management?
Industries such as academic laboratories, pharmaceuticals, chemical manufacturing, hospitals, food and beverage, and government facilities rely on these systems.
How does remote monitoring improve chemical inventory management?
Remote monitoring provides real-time data on inventory levels, sends automatic alerts for low stocks, and reduces the need for manual checks, enhancing efficiency and safety.
What are the key components of a chemical inventory system?
Key components include tracking and monitoring, data management, safety and compliance, and resource optimization.
How does a chemical inventory system support regulatory compliance?
It maintains accurate records, proper labeling, and accessible SDS, ensuring adherence to regulations like OSHA’s Hazard Communication Standard.
What challenges are associated with chemical inventory management?
Challenges include maintaining data accuracy, integrating systems, and managing implementation costs, which can be addressed through training and careful planning.